Smart City – simplifies the management of urban processes and increases the comfort of life. 
It has been the subject of discussion for many years. In Ukraine, strategic approaches to the transition to the smart status of million-plus cities are increasingly being used.
Smart City is a holistic concept of smart integration of information and communication technologies for monitoring and managing urban infrastructure.
The goal of a smart city is to optimize the costs of a number of highly exploited resources, improve people’s lives by increasing the level of comfort and safety, the quality and efficiency of service in various areas.
Smart City technologies and their purpose
The Smart City concept is characterized by three basic parameters:
- Manufacturability.
- Intellectualization.
- Focus on lifestyle. A “smart city” should be environmentally friendly, safe, energy-intensive, open up wide opportunities and provide the most comfortable life.
Among the priority sectors in need of intellectual modernization are public administration, city infrastructure and the economy. The main directions of development of these sectors are presented below.
Innovation economy
City infrastructure
Public administration
- Innovations in industry, clusters, city districts
- Smart workforce: Education and employment
- Creation of knowledge-intensive companies
- Transport
- Energy/Utilities
- Environmental Protection/Safety
- Administrative services to citizens
- Representative and direct democracy
- Citizen Services: Quality of Life
General recommendations for the implementation of Smart City systems

- Reassessment of the role of the city and its administration in the life of every citizen as a potential user of smart technologies;
- Development of interrelated integrated approaches to the implementation of projects in order to cover as many spheres of life of citizens in the city as possible;
- Ensuring data security;
- Exclusion of isolated and outdated solutions in favor of the application and development of new advanced automated systems;
- Encouragement of initiative groups and organizations acting as developers of innovative models for the functioning of a modern city;
- Creation of a comprehensive data strategy and data platforms for the implementation of projects in this direction;
- Creation of innovative laboratories to stimulate new developments aimed at saving the ecosystem and increasing the level of comfort and safety of citizens;
- Involvement of representatives of urban infrastructure in the development, financing and implementation of initiatives aimed at the introduction of “smart city” systems;
- Involvement of citizens and other stakeholders in the form of state, public and business institutions;
- Providing political support for relevant projects and the process of their integration into society;
- Creation of a coordinating body and a special system for planning decision-making on the introduction of innovative technologies.
LoRaWAN network the way for a smart city
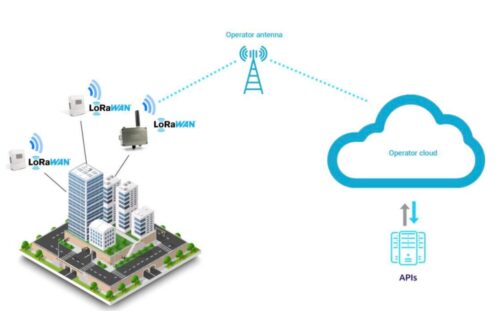 LoRa technology offers technical and economic benefits for smart city applications. LoRa and LoRaWAN provide intelligent monitoring and control infrastructure. This allows us to efficiently collect and analyze data from thousands of networked devices and systems. With this information, for example, they should be able to better decide which services are right for their plans.
LoRa technology offers technical and economic benefits for smart city applications. LoRa and LoRaWAN provide intelligent monitoring and control infrastructure. This allows us to efficiently collect and analyze data from thousands of networked devices and systems. With this information, for example, they should be able to better decide which services are right for their plans.
For densely populated metropolitan areas, it is beneficial that LoRaWAN signals penetrate relatively deep into urban areas. Smart city technologies are changing the image of cities, authorities and citizens interact.
LoRaWAN on the example of smart lighting
 With a LoRa network, sensors can be integrated into any street lighting system that controls lighting and collects usage data. And LoRa technology collects data on all nearby street lights through LoRaWAN. The gateway then sends the information to a public or private cloud server, which analyzes the data, ultimately manages the lighting, and automatically generates warnings for power outages and other faults when needed. Alerts for burnt out lamps and other faults as needed.
With a LoRa network, sensors can be integrated into any street lighting system that controls lighting and collects usage data. And LoRa technology collects data on all nearby street lights through LoRaWAN. The gateway then sends the information to a public or private cloud server, which analyzes the data, ultimately manages the lighting, and automatically generates warnings for power outages and other faults when needed. Alerts for burnt out lamps and other faults as needed.
Users can even add over-the-air (OTA) updates to switch between public and private networks as needed. The bi-directional communication of LoRa technology makes this possible. The range of applications of LoRa technology in smart cities is extremely diverse and is not limited to lighting. The technology can be used in different ways:
- Parking;
- Traffic flow;
- Service of traffic lights;
- Preventive maintenance;
- Recycling;
- Noise and air pollution.
